
Reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions1,2
Adhering to Tivdak Premedication and Required Eye Care may help to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions for your patients.
INDICATION: TIVDAK® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (r/mCC) with disease progression on or after chemotherapy.

Adhering to Tivdak Premedication and Required Eye Care may help to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions for your patients.
Partner with an eye care provider
Prescribe topical eye drops

Corticosteroid Eye Drops*
1 drop per eye or as prescribed

Vasoconstrictor Eye Drops
3 drops per eye immediately prior to infusion or as prescribed

Lubricating Eye Drops
As needed for the duration of therapy and for 30 days after the last dose of Tivdak (available over the counter)
Advise patients on self care at home
Tivdak Infusion Day Timeline (once every 3 weeks)
Chair Time

72 Hours Post Infusion
Remainder of Infusion Day
Day 2
Day 3

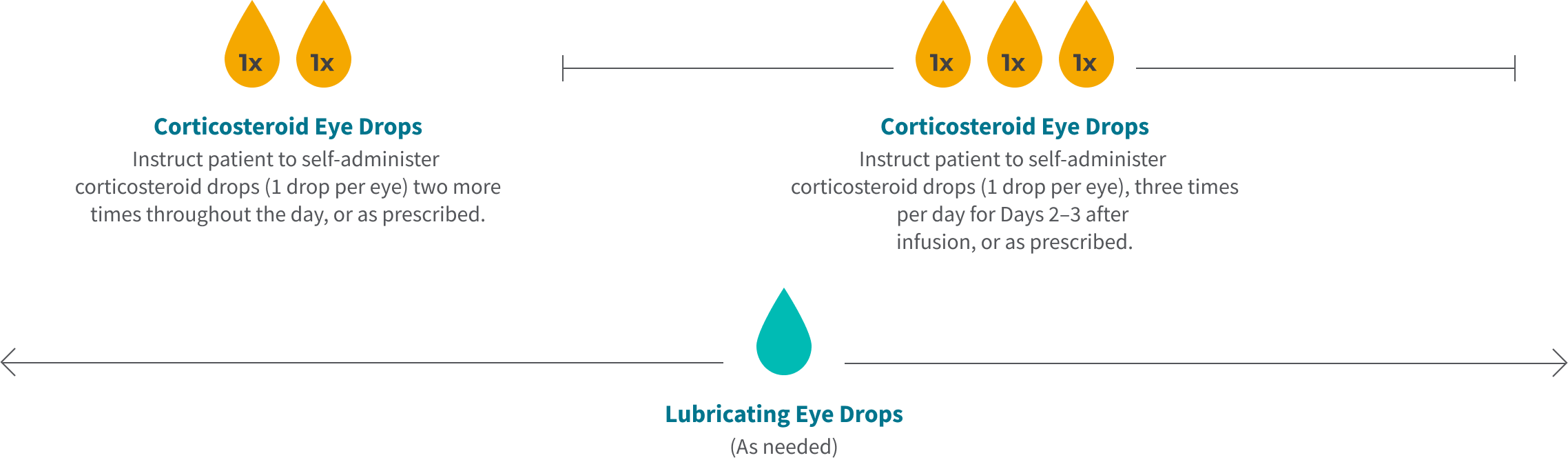
*The initial prescription and all renewals of any corticosteroid medication should be made only after examination with a slit lamp.
Across clinical trials
At last follow-up, patients who experienced ocular adverse reactions had
complete resolution 59% or partial improvement 31%
Partial improvement was defined as a decrease in severity by 1 or more grades from the worst grade.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 55% of patients with cervical cancer treated with Tivdak across clinical trials. The most common ocular adverse reactions were conjunctivitis (32%), dry eye (24%), keratopathy (17%), and blepharitis (5%). Grade 3 ocular adverse reactions occurred in 3.3% of patients, including severe ulcerative keratitis in 1.2% of patients. Nine patients (2.1%) experienced ulcerative keratitis (including 1 with perforation requiring corneal transplantation), 6 (1.4%) conjunctival ulcer, 4 (0.9%) corneal erosion, 2 (0.5%) conjunctival erosion, and 2 (0.5%) symblepharon.
Manage patient treatment with dose modifications

Learn about a support program that helps your patients stay on track with eye care

See phase 3 clinical trial results

References: 1. TIVDAK [Prescribing Information]. Bothell, WA: Seagen Inc. April 2024. 2. Kim SK, Ursell P, Coleman RL, Monk BJ, Vergote I. Mitigation and management strategies for ocular events associated with tisotumab vedotin. Gynecol Oncol. 2022;165(2):385-392.
By clicking this link, you will be redirected to a website that is neither owned nor controlled by Pfizer. Pfizer is not responsible for the content or services of this site.
Tisotumab vedotin-tftv (Tivdak) is now the ONLY NCCN CATEGORY 1 PREFERRED option for second-line or subsequent therapy for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®).
See referenceTIVDAK can cause severe ocular toxicities resulting in changes in vision, including severe vision loss, and corneal ulceration. Conduct an ophthalmic exam, including an assessment of ocular symptoms, visual acuity, and slit lamp exam of the anterior segment of the eye prior to initiation of TIVDAK, prior to every cycle for the first nine cycles, and as clinically indicated. Adhere to the required premedication and eye care before, during, and after infusion. Withhold TIVDAK until improvement and resume, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue, based on severity.
Ocular adverse reactions: TIVDAK can cause severe ocular adverse reactions, including conjunctivitis, keratopathy (keratitis, punctate keratitis, and ulcerative keratitis), and dry eye (increased lacrimation, eye pain, eye discharge, pruritus, irritation, and foreign body sensation), that may lead to changes in vision and/or corneal ulceration.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 55% of patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common were conjunctivitis (32%), dry eye (24%), keratopathy (17%), and blepharitis (5%). Grade 3 ocular adverse reactions occurred in 3.3% of patients, including severe ulcerative keratitis in 1.2% of patients. Nine patients (2.1%) experienced ulcerative keratitis (including one with perforation requiring corneal transplantation), six (1.4%) conjunctival ulcer, four (0.9%) corneal erosion, two (0.5%) conjunctival erosion, and two (0.5%) symblepharon.
In innovaTV 301, 8 patients (3.2%) experienced delayed ocular adverse reactions occurring more than 30 days after discontinuation of TIVDAK. These adverse reactions included 3 patients with ulcerative keratitis, and one patient (each) with keratitis, punctate keratitis and corneal erosion, blepharitis and conjunctival hyperemia, conjunctival scar, and conjunctivitis and xerophthalmia.
Refer patients to an eye care provider to conduct an ophthalmic exam prior to initiation of TIVDAK, prior to every cycle for the first nine cycles, and as clinically indicated. The exam should include visual acuity, slit lamp exam of the anterior segment of the eye, and an assessment of normal eye movement and ocular signs or symptoms which include dry or irritated eyes, eye secretions, or blurry vision.
Adhere to the required premedication and eye care before, during, and after infusion to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions. Monitor for ocular toxicity and promptly refer patients to an eye care provider for any new or worsening ocular signs and symptoms. Withhold, reduce, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity or persistence of the ocular adverse reaction.
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) occurred in 39% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials; 6% of patients experienced Grade 3 PN. PN adverse reactions included peripheral sensory neuropathy (23%), PN (5%), paresthesia (3.8%), peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy (3.3%), muscular weakness (2.8%), and peripheral motor neuropathy (2.4%). One patient with another tumor type treated with TIVDAK at the recommended dose developed Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neuropathy such as paresthesia, tingling or a burning sensation, neuropathic pain, muscle weakness, or dysesthesia. For new or worsening PN, withhold, then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity of PN.
Hemorrhage occurred in 51% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common all grade hemorrhage adverse reaction was epistaxis (33%). Grade 3 hemorrhage occurred in 4% of patients.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage. For patients experiencing pulmonary or central nervous system hemorrhage, permanently discontinue TIVDAK. For Grade ≥2 hemorrhage in any other location, withhold until bleeding has resolved, blood hemoglobin is stable, there is no bleeding diathesis that could increase the risk of continuing therapy, and there is no anatomical or pathologic condition that can increase the risk of hemorrhage recurrence. After resolution, either resume treatment or permanently discontinue TIVDAK.
Pneumonitis that is severe, life-threatening, or fatal can occur in patients treated with antibody-drug conjugates containing vedotin, including TIVDAK. Among cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials, 4 patients (0.9%) experienced pneumonitis, including 1 patient who had a fatal outcome.
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms of pneumonitis. Symptoms may include hypoxia, cough, dyspnea or interstitial infiltrates on radiologic exams. Infectious, neoplastic, and other causes for such symptoms should be excluded through appropriate investigations. Withhold TIVDAK for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2 pneumonitis and consider dose reduction. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis.
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), including events of fatal or life-threatening Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), can occur in patients treated with TIVDAK. SCAR occurred in 1.6% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. Grade ≥3 SCAR occurred in 0.5% of patients, including 1 patient who had a fatal outcome.
Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of SCAR, which include target lesions, worsening skin reactions, blistering or peeling of the skin, painful sores in mouth, nose, throat, or genital area, fever or flu-like symptoms, and swollen lymph nodes. If signs or symptoms of SCAR occur, withhold TIVDAK until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. Early consultation with a specialist is recommended to ensure greater diagnostic accuracy and appropriate management. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK for confirmed Grade 3 or 4 SCAR, including SJS.
Embryo-fetal toxicity: TIVDAK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 2 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 4 months after the last dose.
Across clinical trials of TIVDAK in 425 patients with r/mCC, the most common (≥25%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were hemoglobin decreased (45%), PN (39%), conjunctival adverse reactions (38%), nausea (37%), fatigue (36%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (33%), epistaxis (33%), alopecia (31%), alanine aminotransferase increased (30%), and hemorrhage (28%).
innovaTV 301 Study: 250 patients with r/mCC with disease progression on or after systemic therapy
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 33% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥2%) were urinary tract infection (4.8%), small intestinal obstruction (2.4%), sepsis, abdominal pain, and hemorrhage (each 2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.6% of patients who received TIVDAK, including acute kidney injury, pneumonia, sepsis, and SJS (each 0.4%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 15% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN and ocular adverse reactions (each 6%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 39% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were ocular adverse reactions (16%) and PN (6%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 30% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN and ocular adverse reactions (each 10%). The ocular adverse reactions included conjunctival disorders (4.8%), keratopathy (4%), and dry eye (0.8%).
innovaTV 204 Study: 101 patients with r/mCC with disease progression on or after chemotherapy
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 43% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were ileus (6%), hemorrhage (5%), pneumonia (4%), PN, sepsis, constipation, and pyrexia (each 3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients who received TIVDAK, including septic shock, pneumonitis, sudden death, and multisystem organ failure (each 1%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 13% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN (5%) and corneal adverse reactions (4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 47% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were PN (8%), conjunctival adverse reactions, and hemorrhage (each 4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 23% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were conjunctival adverse reactions (9%) and corneal adverse reactions (8%).
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: Concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) exposure, which may increase the risk of TIVDAK adverse reactions. Closely monitor patients for TIVDAK adverse reactions.
Moderate or severe hepatic impairment: MMAE exposure and adverse reactions are increased. Avoid use.
Lactation: Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during TIVDAK treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING for TIVDAK.
TIVDAK is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (r/mCC) with disease progression on or after chemotherapy.
TIVDAK can cause severe ocular toxicities resulting in changes in vision, including severe vision loss, and corneal ulceration. Conduct an ophthalmic exam, including an assessment of ocular symptoms, visual acuity, and slit lamp exam of the anterior segment of the eye prior to initiation of TIVDAK, prior to every cycle for the first nine cycles, and as clinically indicated. Adhere to the required premedication and eye care before, during, and after infusion. Withhold TIVDAK until improvement and resume, reduce the dose, or permanently discontinue, based on severity.
Ocular adverse reactions: TIVDAK can cause severe ocular adverse reactions, including conjunctivitis, keratopathy (keratitis, punctate keratitis, and ulcerative keratitis), and dry eye (increased lacrimation, eye pain, eye discharge, pruritus, irritation, and foreign body sensation), that may lead to changes in vision and/or corneal ulceration.
Ocular adverse reactions occurred in 55% of patients with cervical cancer treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common were conjunctivitis (32%), dry eye (24%), keratopathy (17%), and blepharitis (5%). Grade 3 ocular adverse reactions occurred in 3.3% of patients, including severe ulcerative keratitis in 1.2% of patients. Nine patients (2.1%) experienced ulcerative keratitis (including one with perforation requiring corneal transplantation), six (1.4%) conjunctival ulcer, four (0.9%) corneal erosion, two (0.5%) conjunctival erosion, and two (0.5%) symblepharon.
In innovaTV 301, 8 patients (3.2%) experienced delayed ocular adverse reactions occurring more than 30 days after discontinuation of TIVDAK. These adverse reactions included 3 patients with ulcerative keratitis, and one patient (each) with keratitis, punctate keratitis and corneal erosion, blepharitis and conjunctival hyperemia, conjunctival scar, and conjunctivitis and xerophthalmia.
Refer patients to an eye care provider to conduct an ophthalmic exam prior to initiation of TIVDAK, prior to every cycle for the first nine cycles, and as clinically indicated. The exam should include visual acuity, slit lamp exam of the anterior segment of the eye, and an assessment of normal eye movement and ocular signs or symptoms which include dry or irritated eyes, eye secretions, or blurry vision.
Adhere to the required premedication and eye care before, during, and after infusion to reduce the risk of ocular adverse reactions. Monitor for ocular toxicity and promptly refer patients to an eye care provider for any new or worsening ocular signs and symptoms. Withhold, reduce, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity or persistence of the ocular adverse reaction.
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) occurred in 39% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials; 6% of patients experienced Grade 3 PN. PN adverse reactions included peripheral sensory neuropathy (23%), PN (5%), paresthesia (3.8%), peripheral sensorimotor neuropathy (3.3%), muscular weakness (2.8%), and peripheral motor neuropathy (2.4%). One patient with another tumor type treated with TIVDAK at the recommended dose developed Guillain-Barre syndrome.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of neuropathy such as paresthesia, tingling or a burning sensation, neuropathic pain, muscle weakness, or dysesthesia. For new or worsening PN, withhold, then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue TIVDAK based on the severity of PN.
Hemorrhage occurred in 51% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. The most common all grade hemorrhage adverse reaction was epistaxis (33%). Grade 3 hemorrhage occurred in 4% of patients.
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemorrhage. For patients experiencing pulmonary or central nervous system hemorrhage, permanently discontinue TIVDAK. For Grade ≥2 hemorrhage in any other location, withhold until bleeding has resolved, blood hemoglobin is stable, there is no bleeding diathesis that could increase the risk of continuing therapy, and there is no anatomical or pathologic condition that can increase the risk of hemorrhage recurrence. After resolution, either resume treatment or permanently discontinue TIVDAK.
Pneumonitis that is severe, life-threatening, or fatal can occur in patients treated with antibody-drug conjugates containing vedotin, including TIVDAK. Among cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials, 4 patients (0.9%) experienced pneumonitis, including 1 patient who had a fatal outcome.
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms of pneumonitis. Symptoms may include hypoxia, cough, dyspnea or interstitial infiltrates on radiologic exams. Infectious, neoplastic, and other causes for such symptoms should be excluded through appropriate investigations. Withhold TIVDAK for patients who develop persistent or recurrent Grade 2 pneumonitis and consider dose reduction. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK in all patients with Grade 3 or 4 pneumonitis.
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), including events of fatal or life-threatening Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), can occur in patients treated with TIVDAK. SCAR occurred in 1.6% of cervical cancer patients treated with TIVDAK across clinical trials. Grade ≥3 SCAR occurred in 0.5% of patients, including 1 patient who had a fatal outcome.
Monitor patients for signs or symptoms of SCAR, which include target lesions, worsening skin reactions, blistering or peeling of the skin, painful sores in mouth, nose, throat, or genital area, fever or flu-like symptoms, and swollen lymph nodes. If signs or symptoms of SCAR occur, withhold TIVDAK until the etiology of the reaction has been determined. Early consultation with a specialist is recommended to ensure greater diagnostic accuracy and appropriate management. Permanently discontinue TIVDAK for confirmed Grade 3 or 4 SCAR, including SJS.
Embryo-fetal toxicity: TIVDAK can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 2 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with TIVDAK and for 4 months after the last dose.
Across clinical trials of TIVDAK in 425 patients with r/mCC, the most common (≥25%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were hemoglobin decreased (45%), PN (39%), conjunctival adverse reactions (38%), nausea (37%), fatigue (36%), aspartate aminotransferase increased (33%), epistaxis (33%), alopecia (31%), alanine aminotransferase increased (30%), and hemorrhage (28%).
innovaTV 301 Study: 250 patients with r/mCC with disease progression on or after systemic therapy
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 33% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥2%) were urinary tract infection (4.8%), small intestinal obstruction (2.4%), sepsis, abdominal pain, and hemorrhage (each 2%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.6% of patients who received TIVDAK, including acute kidney injury, pneumonia, sepsis, and SJS (each 0.4%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 15% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN and ocular adverse reactions (each 6%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 39% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were ocular adverse reactions (16%) and PN (6%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 30% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN and ocular adverse reactions (each 10%). The ocular adverse reactions included conjunctival disorders (4.8%), keratopathy (4%), and dry eye (0.8%).
innovaTV 204 Study: 101 patients with r/mCC with disease progression on or after chemotherapy
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 43% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were ileus (6%), hemorrhage (5%), pneumonia (4%), PN, sepsis, constipation, and pyrexia (each 3%). Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 4% of patients who received TIVDAK, including septic shock, pneumonitis, sudden death, and multisystem organ failure (each 1%).
Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 13% of patients receiving TIVDAK; the most common (≥3%) were PN (5%) and corneal adverse reactions (4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose interruption occurred in 47% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were PN (8%), conjunctival adverse reactions, and hemorrhage (each 4%). Adverse reactions leading to dose reduction occurred in 23% of patients; the most common (≥3%) were conjunctival adverse reactions (9%) and corneal adverse reactions (8%).
Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: Concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase unconjugated monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) exposure, which may increase the risk of TIVDAK adverse reactions. Closely monitor patients for TIVDAK adverse reactions.
Moderate or severe hepatic impairment: MMAE exposure and adverse reactions are increased. Avoid use.
Lactation: Advise lactating women not to breastfeed during TIVDAK treatment and for at least 3 weeks after the last dose.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including BOXED WARNING for TIVDAK.
TIVDAK is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (r/mCC) with disease progression on or after chemotherapy.